In the world of software development, the ability to deliver updates quickly and reliably can make or break a product. Enter Continuous Deployment (CD), a practice that ensures every change to the codebase is automatically deployed to production once it passes automated tests. Sound revolutionary? It is! Let’s explore what CD is, why it matters, and how you can adopt it.
What is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment is the practice of automatically deploying software changes to production without manual intervention. It builds on Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery, ensuring that once a change passes all automated tests, it goes live.
Unlike Continuous Delivery, where a human may approve a release, Continuous Deployment eliminates this step, embracing full automation.
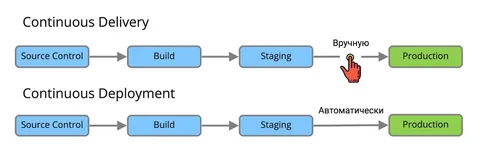
The Evolution of Software Delivery
1. Traditional Approach
Releases were infrequent and often plagued by delays and bugs.
2. Continuous Delivery
Focused on automating everything up to the deployment phase but required manual approval.
3. Continuous Deployment
Takes automation to the next level, deploying changes directly to production as soon as they’re ready.
Why is Continuous Deployment Important?
In today’s fast-paced tech environment, speed and reliability are critical. Continuous Deployment offers several key benefits:
1. Faster Time-to-Market
Deliver features and fixes to users quickly, gaining a competitive edge.
2. Higher Quality
Automated testing ensures only reliable changes are deployed.
3. Reduced Manual Errors
Automation removes the risks associated with human intervention.
4. Increased Customer Satisfaction
Frequent updates keep users happy and engaged.
How Continuous Deployment Works
The Continuous Deployment pipeline consists of several key stages:
1. Code Commit
Developers push code changes to a shared repository, like GitHub or GitLab.
2. Continuous Integration (CI)
CI tools automatically build the code and run a series of tests.
3. Automated Testing
Changes are validated against unit, integration, and end-to-end tests.
4. Deployment
If the tests pass, the CD pipeline deploys the changes to the production environment automatically.
5. Monitoring and Feedback
Post-deployment, monitoring tools track the performance and detect any issues.
Key Principles of Continuous Deployment
- Automation: From testing to deployment, everything is automated.
- Reliable Testing: A robust test suite is critical to ensure code quality.
- Incremental Changes: Deploy small, frequent updates to reduce risk.
- Continuous Monitoring: Keep a close eye on performance and user feedback.
- Rollback Mechanisms: Have plans in place to quickly revert changes if something goes wrong.
Popular Continuous Deployment Tools
| Tool | Features |
|---|---|
| Jenkins | Open-source, highly extensible |
| GitLab CI/CD | Built-in CD features with GitLab repositories |
| CircleCI | Fast builds and deployment pipelines |
| Spinnaker | Focused on multi-cloud deployments |
| AWS CodePipeline | Seamless integration with AWS infrastructure |
Benefits of Continuous Deployment
1. Seamless User Experience
Updates are rolled out incrementally, reducing downtime and disruption.
2. Developer Productivity
By automating repetitive tasks, developers can focus on writing code.
3. Faster Feedback Loops
Changes reach users quickly, allowing for rapid feedback and iteration.
4. Scalability
CD pipelines can handle large volumes of updates effortlessly.
Challenges of Continuous Deployment
1. Test Coverage
Incomplete or unreliable tests can lead to bugs slipping into production.
2. Cultural Shift
Teams need to embrace automation and trust in the system.
3. Complexity
Building a robust CD pipeline requires time and expertise.
4. Security Risks
Automating deployments can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
Best Practices for Continuous Deployment
- Build a Strong Test Suite
Cover all aspects of functionality, performance, and security. - Monitor Everything
Use tools like Prometheus, Datadog, or Splunk to track metrics and detect issues. - Deploy Incrementally
Use techniques like blue-green deployments or canary releases to minimize risk. - Collaborate Cross-Functionally
Ensure that developers, testers, and operations work closely together. - Learn from Failures
Every failure is an opportunity to improve the pipeline and processes.
Continuous Deployment vs. Continuous Delivery
| Aspect | Continuous Deployment | Continuous Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Fully automated deployment to production | Automated testing, manual approval for deployment |
| Human Intervention | None | Required for final deployment step |
| Speed | Faster | Slightly slower |
| Use Case | Ideal for frequent, small updates | Better for high-risk environments |
Real-World Examples of Continuous Deployment
1. Netflix
Netflix’s CD pipeline deploys code changes thousands of times daily, ensuring a seamless streaming experience for millions of users.
2. Facebook
Facebook uses CD to roll out updates quickly, testing changes on small user groups before full deployment.
3. Etsy
Etsy’s commitment to CD has improved their ability to deliver features rapidly, with minimal downtime.
The Future of Continuous Deployment
1. AI-Powered Pipelines
Artificial intelligence will optimize pipelines, predicting failures before they occur.
2. Security-First CD
Integrating advanced security tools directly into pipelines to detect and prevent vulnerabilities.
3. Serverless Deployment
CD in serverless environments will reduce infrastructure complexity.
Getting Started with Continuous Deployment
- Start with CI: Ensure a solid Continuous Integration process is in place.
- Automate Tests: Build a comprehensive test suite to validate changes.
- Select the Right Tools: Choose tools that integrate seamlessly with your stack.
- Monitor and Learn: Use monitoring tools to refine the process and address issues proactively.
- Adopt Gradually: Start with low-risk projects and expand as your team gains confidence.
Final Thoughts
Continuous Deployment is a powerful practice that brings speed, efficiency, and reliability to software delivery. While it requires a strong commitment to automation and quality, the rewards are worth it. Ready to transform your software delivery process? Dive into Continuous Deployment and experience the future of development today!